
General characteristics of pelvic fracture include severe pain, pelvic bone instability and associated internal bleeding. The pelvis consists of three major bones joined together in a ringed shape and held by strong ligaments (see figure 1). Pelvic stability provides comfort, decreases hemorrhage and facilitates patient mobilization.Ĭharacteristics of pelvic fracture Click to enlarge

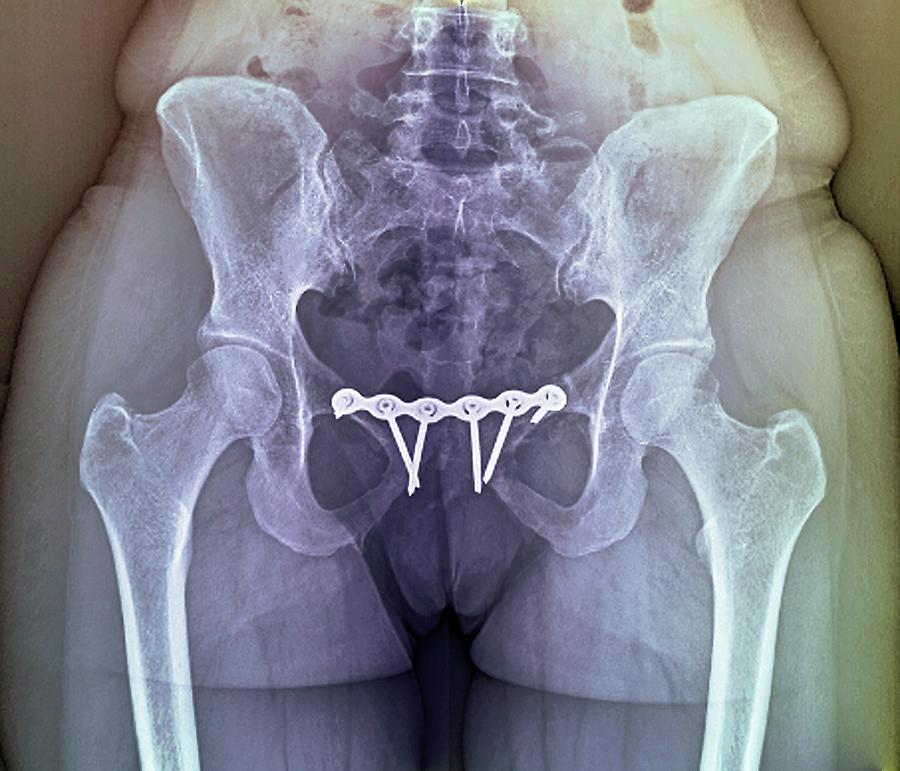
Both external (outside the skin) and internal (located in or on the bone) fixations are advocated. Pelvic bone fixation provides stability to the pelvic bone and promotes natural healing of the fracture.Displaced (misaligned) fractures and dislocations of the pelvic ring can be stabilized with various surgical techniques.Ī variety of surgical techniques are used to stabilize pelvic ring disruptions (fractures and/or dislocations). Surgical intervention may be employed for fixation of the fractured pelvic bones using screws and plates. The treatment of unstable fractures includes management of the bleeding and injuries of the internal organs, blood vessels, and nerves. These methods may take 8–12 months for complete healing. Minor or stable fractures can be treated with conservative methods such as rest, medications, use of crutches, physical therapy, and if required minor surgery. Treatment of the pelvic fracture depends upon the severity of the injury and condition of the patient. In some cases, additional contrasting studies using radioactive dye may be recommended to evaluate the structural and functional activity of organs such as the urethra, bladder, and the pelvic blood vessels. Imaging techniques such as X-rays, CT (Contrast Tomography) and MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan may also be used to confirm the exact condition or breakage of the pelvic bones. The diagnosis of pelvic fracture starts with physical examination including checking the functional activity of the various body organs present in the pelvic region. Bleeding through the urethra or vagina and the rectum.Pain and swelling in the groin or hip region that may worsen with ambulation.The common symptoms associated with pelvic fractures are: Accidental injury or fall from a great height.Conditions such as osteoporosis, especially in elderly people.The common causes responsible for pelvic fractures include: It requires immediate medical care followed by long-term physical therapy and rehabilitation. Unstable pelvic fractures may cause shock, extensive internal bleeding, and damage to the internal organs. Unstable Pelvic Fractures: Have breakage at two or more points, followed by severe bleeding.Stable Pelvic Fractures: Have single point breakage in the pelvis ring and broken bones remain in position shows less bleeding.The pelvis ring also acts as point of attachment for muscles approaching from the upper and lower part of the body.īased on the damage of the pelvis ring and associated structures, pelvic fractures can be categorized as:

Also, several large nerves and blood vessels supplying the lower limbs pass through the pelvis. Various organs related to the digestive and reproductive systems lie within the pelvis ring. The side of the pelvis is composed of a cup shape socket, known as acetabulum. The pelvis is composed of three bones, namely ilium, ischium, and pubis that are fused together. The pelvis is a round structure of bones located at the base of the spine, connected to the sacrum of the spine with the help of strong ligaments.
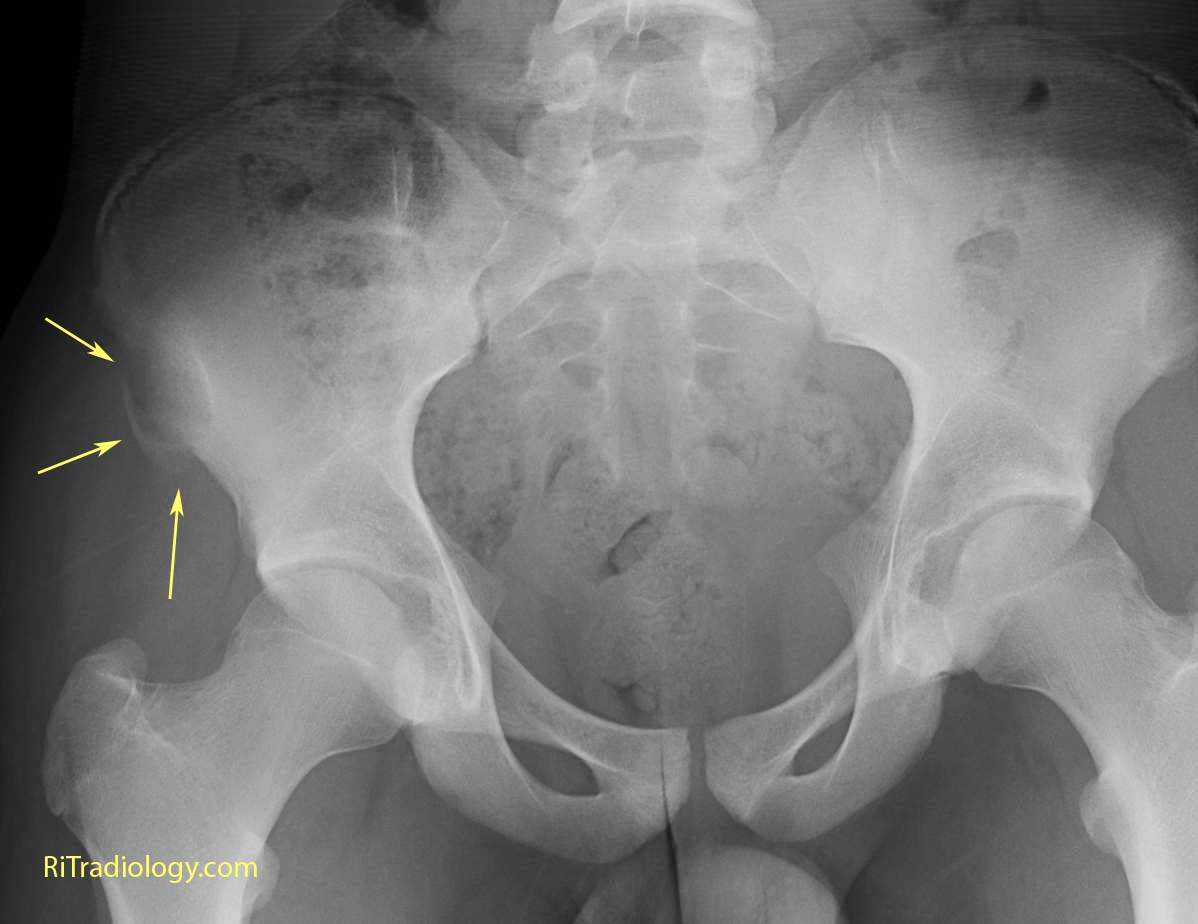
It may damage internal organs, nerves, and blood vessels associated with the pelvis region. Pelvic fracture is a condition that arises due to breakage of the pelvis bones.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
